Hip pain involves any pain in or around the hip joint. You may not feel pain from your hip directly over the hip area. You may feel it in your groin or pain in your thigh or knee.
Hip Injuries
Hip fractures can be caused by a variety of factors, including falls, osteoporosis (a condition in which bones become weak and brittle), and underlying medical conditions that weaken bones. Hip fractures can be caused by a variety of factors, including falls, osteoporosis (a condition in which bones become weak and brittle), and underlying medical conditions that weaken bones.
Symptoms of a hip fracture may include:
- Severe pain in the hip or groin area
- Swelling and tenderness in the affected area
- Inability to put weight on the affected leg
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint
- The affected leg may appear shorter or turned outward
- Maintain good bone health
- Take steps to prevent falls by ensuring a safe environment
- Remove tripping hazards from your home, such as loose rugs or clutter.
- Use non-slip mats in the bathroom and grab bars near the toilet and shower.
- Install handrails on staircases and ensure they are in good condition.
- Adequately light hallways, stairs, and rooms.
- Wear appropriate footwear with non-slip soles and good support.
- Consider using assistive devices like canes or walkers if necessary.
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve strength, balance, and coordination.
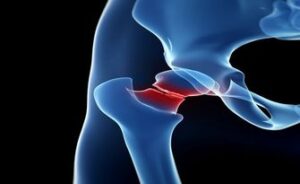
Arthritis of Hip
Arthritis of the hip is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in the hip joint. There are several types of arthritis that can affect the hip, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis and is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time. In the hip, osteoarthritis can cause the cartilage that cushions the joint to wear down, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage. In the hip, rheumatoid arthritis can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, as well as a feeling of warmth or tenderness in the affected area.
Post-traumatic arthritis can occur after a hip injury, such as a fracture or dislocation, and can cause pain and stiffness in the joint over time.
Symptoms of hip arthritis may include:
- Pain in the hip or groin area
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint
- A clicking or grinding sensation in the hip during movement
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected area
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce the load on your hips.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercises that promote joint flexibility, strength, and stability. Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga can help maintain joint health and reduce the risk of hip arthritis
- Avoid repetitive stress and overuse injuries
- Maintain good posture to minimize unnecessary stress on the hip joints
- Use proper technique during exercise and physical activities and avoid sudden, jerky movements that can strain the hip joints.
- Protect your hips during falls or accidents

Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of Hip Joint
Avascular necrosis (AVN) of the hip, also known as osteonecrosis, is a condition in which the bone tissue in the hip joint dies due to a lack of blood supply. This can cause the bone to collapse, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the hip joint.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of AVN of the hip, including:
- Trauma to the hip joint, such as a fracture or dislocation
- Long-term use of corticosteroid medications
- Alcohol abuse
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medical conditions, such as sickle cell anemia or lupus
Symptoms of AVN of the hip may include:
- Pain in the hip or groin area, which may be mild at first and worsen over time
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint
- A limp or difficulty walking
- The affected leg may appear shorter or turned outward
- Certain medical conditions and treatments can increase the risk of AVN. If you have conditions such as lupus, sickle cell disease, or HIV/AIDS, or if you are undergoing treatment such as radiation therapy or long-term corticosteroid use, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions and minimize their impact on your bone health.
- Excessive alcohol consumption is a known risk factor for AVN, particularly in the hip joint.
- Avoid trauma to hip joint because trauma to the bones and joints can disrupt blood supply and increase the risk of AVN
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Monitor and manage joint health
Trochanteric Bursitis
Trochanteric bursitis is a condition in which the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac near the hip joint, becomes inflamed and painful. The trochanteric bursa is located on the outside of the hip and helps cushion the muscles and tendons that pass over the greater trochanter, a bony protrusion on the side of the hip.
Trochanteric bursitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, injury, or underlying medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. It is more common in women and in older adults.
Symptoms of trochanteric bursitis may include:
- Pain or tenderness on the outside of the hip or thigh
- Pain that may radiate down the outside of the leg
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint
- Aching or burning sensation in the affected area
- Avoid repetitive activities that involve repetitive hip movements or excessive pressure on the hips.
- Engage in regular stretching exercises to maintain flexibility in the ankles and surrounding muscles to prevent stiffness around the ankle
- Strengthening the muscles around the Hip joint can provide better support and stability
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercises or sports to allow your body to adapt and avoid overuse injuries.
- Incorporate cross-training and alternate between different activities to avoid overuse of the area around the Hip
- Maintain a healthy weight of the body
- Prior to engaging in physical activity or exercise, warm up your muscles and tendons with light aerobic exercises and dynamic stretches.
Labral Tear or SLAP Tear of Hip
A labral tear of the hip occurs when the labrum, a piece of cartilage that lines the hip joint, is torn. The labrum helps cushion and stabilize the hip joint, and a tear can cause pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the hip.
Labral tears of the hip can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, injury, or underlying medical conditions such as hip dysplasia or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI).
Symptoms of a labral tear of the hip may include:
- Pain in the hip or groin area, which may be sharp or dull
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip joint
- A clicking or popping sensation in the hip during movement
- A feeling of instability in the hip joint
- Avoid repetitive activities that involve repetitive hip movements or excessive pressure on the hips.
- Engage in regular stretching exercises to maintain flexibility in the ankles and surrounding muscles to prevent stiffness around the ankle
- Strengthening the muscles around the Hip joint can provide better support and stability
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercises or sports to allow your body to adapt and avoid overuse injuries.
- Incorporate cross-training and alternate between different activities to avoid overuse of the area around the Hip
- Maintain a healthy weight of the body
- Prior to engaging in physical activity or exercise, warm up your muscles and tendons with light aerobic exercises and dynamic stretches.
YOUR NEXT STEPS!
-
Request An Appointment
-
Find the Root Cause and Receive A Custom Treatment Plan
-
Monitor Progress
-
Recover & Get Back to Life!