Elbow pain is often caused by overuse or injury. Many sports, hobbies and jobs require repetitive hand, wrist or arm movements. Elbow pain can be the result of problems with bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments or joints.
Elbow Pain
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition that causes pain and tenderness in the outer part of the elbow. Despite its name, this condition can occur in anyone who performs repetitive motions with the wrist and arm, not just tennis players.
The exact cause of tennis elbow is related to overuse and repetitive stress on the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle, a bony bump on the outer part of the elbow. This can lead to small tears in the tendon, causing pain and inflammation.
Symptoms of tennis elbow may include:
- Pain or tenderness on the outer part of the elbow
- Weakness in the affected arm or wrist
- Difficulty with gripping or lifting objects
- Stiffness or soreness in the elbow joint
- Pain that worsens with activity or when lifting objects
- Before engaging in any activities that involve repetitive arm motions, such as playing tennis or other sports, take time to warm up your muscles.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises that specifically target the forearm muscles to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises that specifically target the forearm muscles to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Strengthening the muscles in your forearm can help prevent tennis elbow. Incorporate exercises that target the forearm muscles into your fitness routine.
- If you engage in activities that involve repetitive arm motions, take regular breaks to rest your forearm muscles. Avoid prolonged and continuous use of the muscles without giving them time to recover.
- If you participate in sports or activities that put a significant strain on your forearm, consider modifying your techniques or using alternative grips to reduce stress on the muscles and tendons
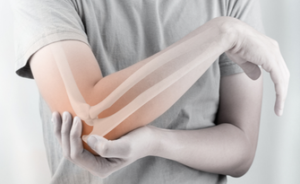
Golfer's Elbow
Golfer’s elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition that causes pain and tenderness in the inner part of the elbow. Despite its name, this condition can occur in anyone who performs repetitive motions with the wrist and arm, not just golfers.
The exact cause of golfer’s elbow is related to overuse and repetitive stress on the tendons that attach to the medial epicondyle, a bony bump on the inner part of the elbow. This can lead to small tears in the tendon, causing pain and inflammation.
Symptoms of golfer’s elbow may include:
- Pain or tenderness on the inner part of the elbow
- Weakness in the affected arm or wrist
- Difficulty with gripping or lifting objects
- Stiffness or soreness in the elbow joint
- Pain that worsens with activity or when lifting objects
- Before engaging in any activities that involve repetitive arm motions, such as playing tennis or other sports, take time to warm up your muscles.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises that specifically target the forearm muscles to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises that specifically target the forearm muscles to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
- Strengthening the muscles in your forearm can help prevent tennis elbow. Incorporate exercises that target the forearm muscles into your fitness routine.
- If you engage in activities that involve repetitive arm motions, take regular breaks to rest your forearm muscles. Avoid prolonged and continuous use of the muscles without giving them time to recover.
- If you participate in sports or activities that put a significant strain on your forearm, consider modifying your techniques or using alternative grips to reduce stress on the muscles and tendons

Olecranon Bursitis
Olecranon Bursitis is a condition that causes inflammation and swelling of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac located at the tip of the elbow. This condition can be caused by trauma, infection, or repetitive motion and it can result in pain and limited range of motion in the affected arm.
Symptoms of elbow bursitis may include:
- Pain or tenderness at the tip of the elbow
- Swelling or a visible bump at the tip of the elbow
- Limited range of motion in the affected arm
- Redness or warmth around the affected area
- Fever or chills in cases of infection
- Avoid excessive pressure or trauma to the elbow
- If you participate in activities or sports that involve a risk of elbow injury or trauma, consider using protective equipment such as elbow pads or guards
- If your work or daily activities involve repetitive movements or prolonged periods of elbow stress, take regular breaks to rest your elbows.
- Practice good posture and ergonomics when sitting or working for extended periods. Ensure that your workstation is properly set up to minimize strain on the elbows
- Avoid excessive weightlifting or heavy lifting
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that occurs when the ulnar nerve in the elbow becomes compressed or irritated. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected arm and hand.
Symptoms of ulnar nerve compression may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the ring and little fingers
- Pain or discomfort in the elbow or forearm
- Weakness in the hand or difficulty with gripping or holding objects
- A feeling of “pins and needles” in the affected area
- Difficulty with fine motor skills such as buttoning a shirt or typing on a keyboard
- Avoid leaning on your elbows for extended periods, as this can compress the ulnar nerve. If you frequently rest your elbows on a hard surface, use a cushion or pad to reduce the pressure.
- Avoid sleeping with your elbows bent for prolonged periods.
- Practice proper lifting techniques
- Regularly perform exercises to strengthen the muscles around the elbow and wrist.
- Take regular breaks
- Maintain a healthy weight
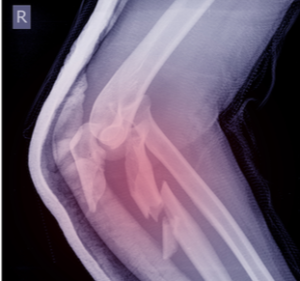
Fractures of Elbow
An elbow fracture is a break in one or more of the bones that make up the elbow joint. The elbow joint is made up of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the radius (one of the forearm bones), and the ulna (the other forearm bone).
Symptoms of an elbow fracture may include:
- Pain or tenderness in the elbow
- Swelling or bruising around the elbow joint
- Stiffness or difficulty moving the arm or elbow
- A popping or cracking sound at the time of injury
- Numbness or tingling in the arm or hand
- Wear protective gear when engaging in sports or activities that carry a risk of falling or impact to the elbow, such as cycling, skateboarding or contact sports
- When participating in sports or physical activities learn and practice proper technique to reduce the risk of falling or sustaining injuries
- Regularly engage in exercises that target the muscles around the elbow joint, such as the biceps, triceps, and forearm muscles
- Avoid overexertion and fatigue
- Warm up and stretch
YOUR NEXT STEPS!
-
Request An Appointment
-
Find the Root Cause and Receive A Custom Treatment Plan
-
Monitor Progress
-
Recover & Get Back to Life!